Cyber Attack and Data Fraud: Marsh-RIMS Study Reveals Top Risks for Indian Companies
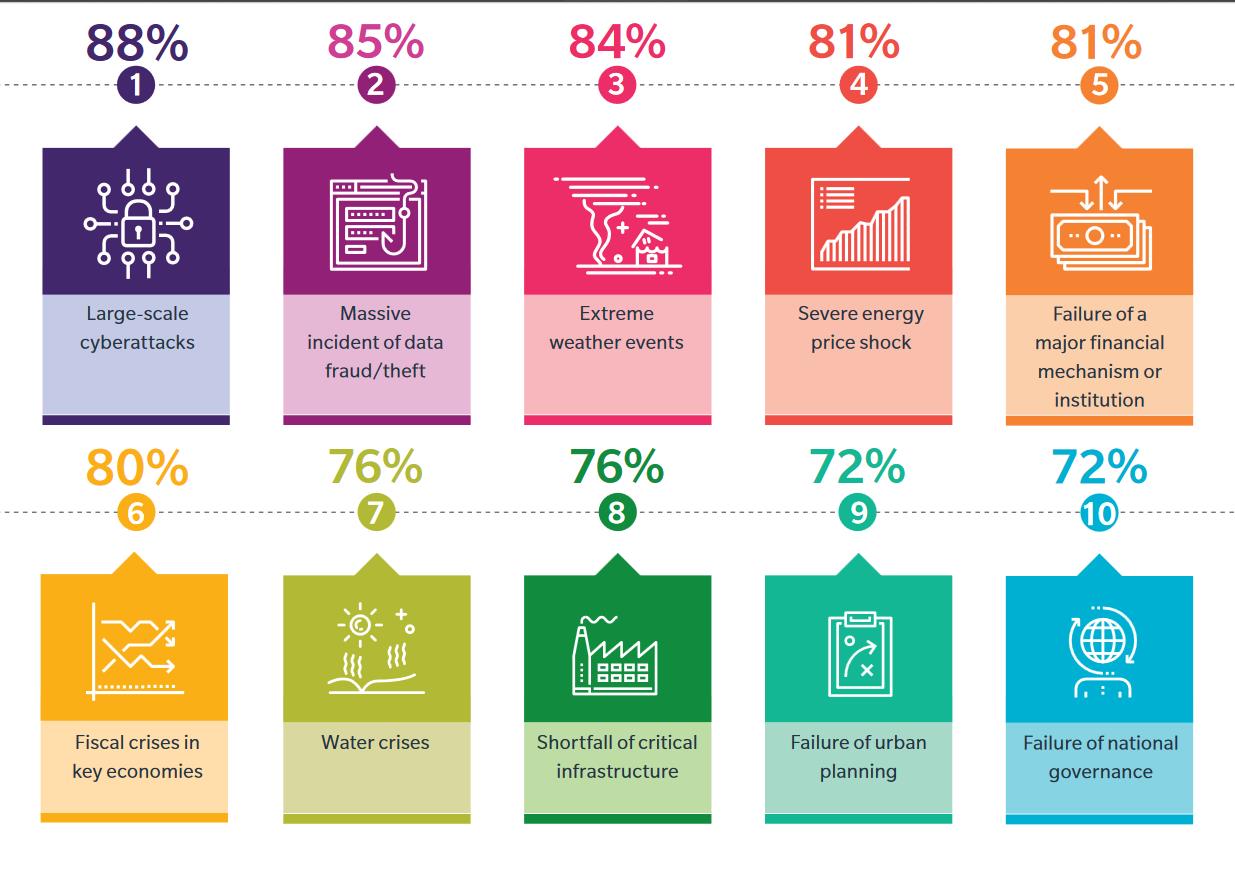
Indian companies trying to embrace the giant wave of digitization have voted large scale cyber attacks and massive incidents of data fraud or theft as the top risks to their businesses (88% and 85% respectively), according to a new report by Marsh and the Risk Management Society (RIMS™). India’s growing dependency on data and digitization has increased the risk of cyberattacks, the report adds.
The devil is in the detail. In May, the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) found that over 22,000 Indian websites, including 114 government portals, had been hacked between April 2017 and January 2018. Furthermore, as reported by The Tribune, high profile data theft incidents such as the breach on Aadhaar, India’s national database, have risk professionals in India questioning whether businesses and the government are adequately prepared to handle cyberattacks and data breaches.
The Marsh-RIMS report, Excellence in Risk Management – State of Risk Management in India, was based on responses from 123 C-suite executives and senior risk professionals from companies spanning 19 industries to an online survey conducted by Marsh and RIMS in September 2018. The survey findings were supplemented with expert input from Marsh & McLennan Companies (MMC) and RIMS.
Extreme weather events (84%), severe energy price shock (81%) and failure in major financial institution (81%) complete the list of the top five risk concerns of the Indian corporates according to the report.
“India faces an increasingly diverse and rapidly evolving risk landscape. The interconnected dynamics of geopolitics, technological advances, global economic integration, social instability, and climate change mean that the manifestation of one risk is increasingly likely to influence others,” Sanjay Kedia, Country Head and CEO of Marsh India said.
Business Critical Risks
The study revealed an increased focus towards the emerging digital and environmental risks. The critical risk areas faced by organizations were classified into three categories:
- Contemporary Risks - Risks which are already of significant concern to organizations. The biggest risks in this category include:
- Severe energy price shock.
- Extreme weather events.
- Imminent Risks - Risks which are likely to be of significant concern to organizations in the next one to three years. The biggest risks in this category include:
- Asset bubble risks.
- Failure of regional or global governance.
- Large-scale cyber-attacks and data frauds.
- Risks on the Horizon - Risks which are likely to be of significant concern for organizations in more than three years. The biggest risks in this category include:
- Social stability.
- Infectious diseases and water crisis.
These are just a few of the many emerging risks that will affect the business environment in India. The interaction of longstanding and emerging risks is creating even more unique and unpredictable risks in a manner that is making it difficult for organizations to even identify risks. Indian organizations, and especially their risk functions, need to be prepared to face such risks. Organizations need to be more proactive in keeping up to date about emerging risks. They can do this through greater interactions with their brokers and by participating at events and forums where risk management knowledge and best practices are shared.
(*Source: Marsh RIMS Excellence in Risk Management – State of Risk Management in India)
